권장 브라우저 안내
이 웹사이트는 Internet Explorer 9 버전 이상에서만 이용 가능합니다.
편리한 사이트 이용을 위하여 최신 브라우저로 업그레이드해주시기 바랍니다.
이 웹사이트는 Internet Explorer 9 버전 이상에서만 이용 가능합니다.
편리한 사이트 이용을 위하여 최신 브라우저로 업그레이드해주시기 바랍니다.
In contemporary architecture, elevators play a vital role as the sole vertical transportation means, ensuring that passengers can conveniently, safely, and comfortably navigate the building. Additionally, elevators hold such significance that they are considered representative of the building's prestige.
Saehan MRL elevator
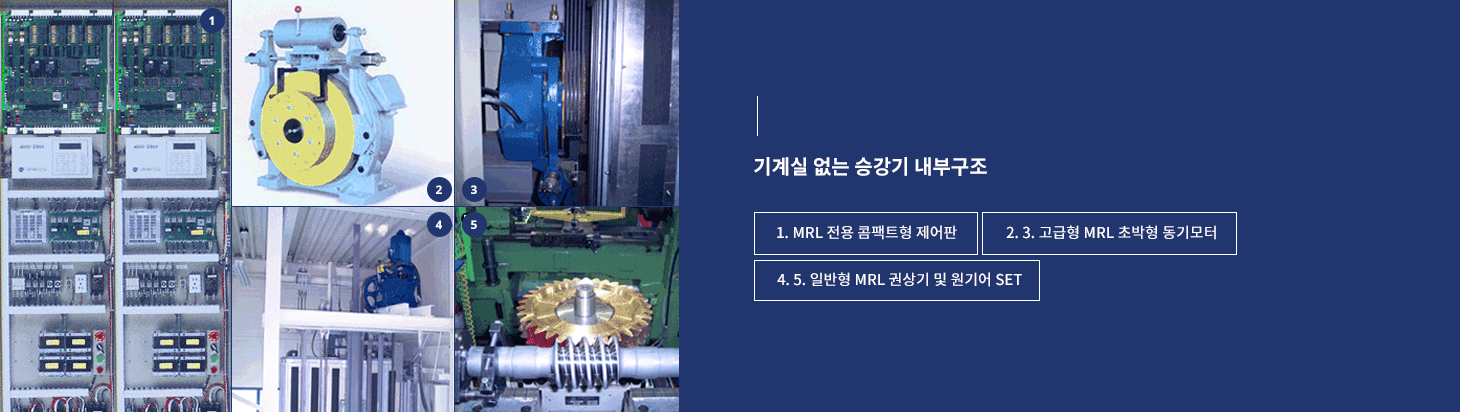
Traditional traction elevators required a dedicated machine room above the elevator shaft to house components such as the hoist machine, control panel, and governor. However, with advanced technology, a groundbreaking innovation has compacted essential components, allowing the installation of all systems within a single elevator shaft, eliminating the need for a machine room

Feature1
Traditional traction elevators required a dedicated machine room above the elevator shaft to house components such as the hoist machine, control panel, and governor. However, with advanced technology, a groundbreaking innovation has compacted essential components, allowing the installation of all systems within a single elevator shaft, eliminating the need for a machine room
Saehan go forth into the world to constant technological development
Feature2
The lack of a protruding machine room on the building's rooftop and fewer height constraints provide opportunities for a more sophisticated and diverse design. This approach aligns well with contemporary trends that emphasize urban design aesthetics and complies with regulations related to height restrictions.
Unlike conventional elevators with machine rooms that may cause noise disturbances for top-floor residents, the absence of a machine room contributes to a quieter system, minimizing discomfort for occupants.
By utilizing a gearless traction machine with a high-efficiency permanent magnet synchronous motor, typically employed in elevators for buildings with 20 or more floors, the elevator's motor capacity is minimized. This design helps reduce the power infrastructure and overall power consumption for the elevator.
| Category | Feature | Premium (Gearless) | Standard (Geared) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoist System | Type | Gearless | Geared |
| Installation Location | At the Bottom of the Shaft | At the Top of the Shaft | At the Bottom of the Shaft |
| Motor Type | Category | Gearless Synchronous Motor | Induction Motor |
| Power Consumption | Comparison | Low (Approximately 70% less) | Moderate |
| Control Panel | Placement | Compact Inverter Control System, Installed on the Elevator Door Side | |
| Advantages | Noteworthy Characteristics | Low Noise, High Efficiency, Oil-Free | Relatively Lower Cost |
* 산업자원부 기술표준원 2002년 11월 자료
Each component of an elevator has a different lifespan based on usage frequency and maintenance condition. Generally, elevator components can be categorized into parts with permanent usage, such as RAIL and JAMB, components with a lifespan of approximately 10-20 years, including control panels, governors, and hoist machines, and parts with a lifespan of less than 10 years, mainly ropes and operating panels.


If you would like to learn more about our new elevator products from SaeHan Elevator, we invite you to download the product information brochure for a comprehensive overview.